Fabricate Light Emmitting Diodes from Sapphire Wafers
We carrey a large selection of Sapphire Substrates used to  fabricate LEDs for research and production. Send us your specs today for an immediate quote!
fabricate LEDs for research and production. Send us your specs today for an immediate quote!
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
What Sapphire Substrate Specs are Used to Fabricate LED Sensors?
Sapphire substrates are widely used for fabricating LED sensors—particularly for blue, green, and UV LEDs—due to sapphire's excellent insulating properties, high thermal stability, and lattice compatibility with GaN (gallium nitride) and AlGaN materials. Below are the most common sapphire substrate specifications used for LED sensors:
✅ Common Sapphire Substrate Specs for LED Sensors
| Spec Category | Typical Values / Notes |
|---|---|
| Material | Single-crystal Al₂O₃ (sapphire) |
| Crystal Orientation | C-plane (0001) most common; also A-plane (11-20), R-plane (1-102) for specific applications |
| Diameter | 2" (50.8 mm), 3" (76.2 mm), 4" (100 mm), 6" (150 mm) |
| Thickness | 430 µm – 650 µm (depending on diameter and equipment) |
| Surface Finish | Double-side polished (DSP) for better epi growth; sometimes single-side polished (SSP) |
| Flatness | < 10 µm TTV (total thickness variation) typical |
| BOW/Warp | < 30 µm (for 2–4" wafers) |
| Miscut Angle | ≤ 0.2° (to optimize GaN film growth and reduce defects) |
| Surface Roughness | < 1 nm RMS on polished side |
| Edge Type | Rounded or beveled to reduce wafer breakage in handling |
| Back Surface | Sometimes roughened or grooved for stress relief |
| Epi-Ready? | Yes, with cleaning and polishing processes suited for GaN/AlGaN deposition |
🔬 Why Sapphire for LED Sensors?
-
Lattice compatibility with GaN epitaxial layers
-
High optical transparency in UV and visible range
-
Thermal and chemical stability under high-temperature MOCVD processes
-
Electrical insulation (acts as an excellent dielectric)
-
High mechanical strength
📌 Notes:
-
C-plane sapphire is the industry standard for GaN-based LED sensors due to its minimal lattice mismatch along the [0001] direction.
-
Patterned Sapphire Substrates (PSS) are also commonly used in high-efficiency LED sensors to enhance light extraction and reduce dislocation density.
Here’s a comparison chart of sapphire vs other common substrates used in LED sensor fabrication, followed by a visual diagram request setup if you’d like it generated.
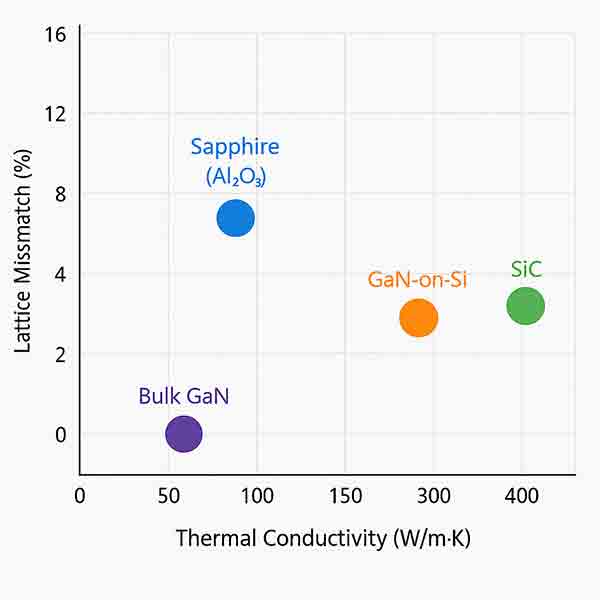
✅ Substrate Comparison for LED Sensors
Property Sapphire (Al₂O₃) SiC (Silicon Carbide) GaN-on-Si (Gallium Nitride on Silicon) Bulk GaN Lattice Match with GaN ~13.9% mismatch ~3.4% mismatch ~16.0% mismatch Perfect Thermal Conductivity ~25 W/m·K ~370 W/m·K ~150 W/m·K (Si) ~130 W/m·K Electrical Conductivity Insulator Semiconductor Conductor Semiconductor Transparency (optical) Transparent (UV–IR) Opaque Opaque Transparent (limited) Cost Low High Moderate Very High Availability Widely available Moderate High Limited Substrate Size Up to 6" common Up to 4" Up to 8" ≤ 2–4" LED Efficiency Moderate to High High Moderate Highest Use Case Mainstream GaN-based LEDs High-performance LEDs Cost-effective mass production Research & high-end
💡 Summary:
-
Sapphire is the most widely used due to availability, transparency, and thermal stability.
-
SiC is used in high-end applications due to better thermal and lattice matching.
-
GaN-on-Si is used in cost-sensitive, large-scale production but with higher defect rates.
-
Bulk GaN provides the best performance but is cost-prohibitive.
-