High-Conformality Oxide Films
When thermal oxidation is too slow or requires too much heat, Tetraethyl Orthosilicate (TEOS) is the industry standard. UniversityWafer, Inc. supplies wafers with precise TEOS oxide layers deposited via PECVD or LPCVD. We provide the high conformality and step coverage needed for Shallow Trench Isolation (STI) and MEMS sacrificial layers.
We stock wafers with pre-deposited TEOS layers:
- ✅ LPCVD TEOS: High Density, Excellent Conformality
- ✅ PECVD TEOS: Low Temperature (<400°C)
- ✅ Thickness: 1,000Å to 5μm+ available
- ✅ Substrates: Silicon, SOI, Quartz, Fused Silica
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Select Your Oxide
- Thermal Oxide Wafers: Highest Quality SiO2.
- Nitride on Silicon: Hard Mask / Passivation.
- SOI Wafers: Device Layer on Oxide.
- Prime Silicon Wafers: The base for all deposition.
Shop by Application
Why switch to TEOS?
- Trench Filling: Excellent step coverage for STI.
- Low Thermal Budget: Deposition at 300°C-700°C (vs 1000°C for Thermal).
- Planarization: Ideal base for CMP processes.
- MEMS: Easy to etch sacrificial layer.
Real-World Scenarios: Solving Deposition Challenges
Case Study 1: Low-Temperature Deposition
Scientist: "I'd like a quote for depositing TEOS by CVD onto an 8” silicon wafer. I need the deposition to be done at or below 200°C to avoid damaging my existing metal layers."
UniversityWafer Solution: "We supplied 8” Wafers with a 2,000Å PETEOS (Plasma Enhanced TEOS) layer. PECVD allows us to deposit high-quality oxide at significantly lower temperatures than LPCVD or Thermal Oxidation, preserving your device structure."
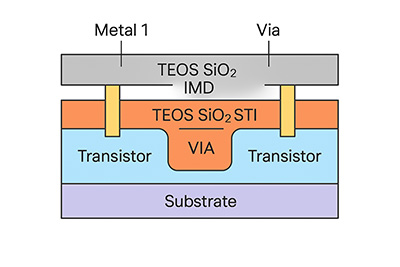
Case Study 2: Intermetal Dielectric (IMD)
Process Engineer: "We need to fill narrow gaps between metal lines. Our current silane-based oxide is leaving voids."
Recommendation: Switch to LPCVD TEOS. TEOS offers superior conformality (step coverage) compared to Silane (SiH4), allowing it to fill high-aspect-ratio gaps without forming voids, making it ideal for IMD layers.
TEOS in Semiconductors
TEOS, or tetraethyl orthosilicate, is a chemical compound widely used in the semiconductor industry, particularly in the process of creating silicon dioxide (SiO₂) layers on substrates. Its chemical formula is Si(OC₂H₅)₄, and it is a liquid precursor for depositing high-purity silicon dioxide films via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes.
Importance of TEOS in Semiconductors
- Silicon Dioxide Formation:
- Silicon dioxide is a critical material in semiconductor devices, serving as an insulator, a gate dielectric in MOSFETs, and a passivation layer.
- TEOS is a key precursor for depositing these SiO₂ layers because it decomposes at high temperatures to form pure SiO₂.
- Process Compatibility:
- TEOS-based deposition works well in plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) processes.
- It enables deposition at relatively low temperatures, making it compatible with devices that cannot tolerate high thermal budgets.
- Uniformity and Conformality:
- TEOS-based CVD processes produce films with excellent step coverage and uniformity, essential for modern devices with complex geometries.
- High Purity:
- TEOS produces SiO₂ with high chemical and structural purity, which is essential for minimizing defects and ensuring device reliability.
- Applications in Nanotechnology:
- TEOS is often used to grow SiO₂ films for advanced micro- and nanofabrication, including biosensors, MEMS devices, and photonic structures.
- Etch Stop and Masking Layer:
- SiO₂ deposited from TEOS acts as an effective etch stop or masking layer in various etching processes.
Key Considerations
- Deposition Parameters: Deposition using TEOS involves careful control of temperature, pressure, and gas flow to achieve desired film properties.
- Environmental and Safety Factors: TEOS is flammable and can hydrolyze in the presence of water to produce ethanol, so proper handling and storage are essential.
In summary, TEOS is a cornerstone material in the semiconductor industry, offering a reliable and versatile method to produce high-quality SiO₂ layers critical for device fabrication. Its role in enabling precise and controlled deposition processes makes it indispensable for advanced semiconductor technologies.
Semiconductor Applications of TEOS
Here are the main semiconductor applications where TEOS is the precursor of choice:
1. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) of SiO₂
- Application: TEOS is a common precursor in Plasma-Enhanced (PECVD) or Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) processes.
- Use Case: Depositing conformal dielectric layers (SiO₂) over complex topographies.
- Advantage: Offers excellent step coverage and uniformity—important for Intermetal Dielectric (IMD) and Shallow Trench Isolation (STI).
2. Shallow Trench Isolation (STI)
- Application: TEOS-based oxide is used to fill trenches that isolate transistors in CMOS devices.
- Why TEOS?: Its deposition and subsequent planarization (via CMP) provide excellent dielectric isolation.
3. Gap Fill and Intermetal Dielectrics
- TEOS oxide helps fill narrow gaps between metal lines in multilevel metallization.
- Used in damascene processes where metal interconnects are embedded in a dielectric matrix.
4. Hard Mask and Sacrificial Layers
- TEOS oxide layers are used as etch masks for patterning underlying layers.
- Can also act as a sacrificial layer in MEMS or nanofabrication, later removed to release structures.
5. Spin-on Glass (SOG) and Sol-Gel Coatings
- Although less common than CVD, TEOS is also used in sol-gel processes to form thin oxide films.
- Particularly useful in low-temperature processing or on substrates sensitive to high temperatures.
6. Silica Nanoparticles and Dielectric Fillers
- In advanced packaging and dielectric materials (e.g. low-k dielectrics), TEOS is a precursor for making silica nanoparticles or composites.
Comparison: LPCVD vs. PECVD for TEOS Oxide
| Feature | LPCVD TEOS | PECVD TEOS |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 650–750°C | ~300–400°C |
| Pressure | Low (0.1–1 Torr) | Low (few Torr) |
| Film Quality | Dense, high-quality oxide | Slightly lower density, may be porous |
| Conformality | Excellent (ideal for trench fill) | Good, but less than LPCVD |
| Deposition Rate | Slower (few hundred Å/min) | Faster (~2000 Å/min or more) |
| Plasma Required? | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Applications | Shallow trench isolation, gate oxides | IMD layers, oxide caps, passivation |
Comparison: TEOS vs. Silane (SiH₄)
| Property | TEOS (Si(OC₂H₅)₄) | Silane (SiH₄) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxide Film | SiO₂ | SiO₂ |
| Deposition Process | LPCVD, PECVD, Spin-on | LPCVD, PECVD |
| Conformality | Very Good | Poor to Moderate |
| By-products | Ethanol-based | Hydrogen-rich |
| Handling | Liquid (Easier to store) | Gas (Flammable/Pyrophoric) |
