MEMS R&D Quote
Ready to fabricate or prototype your MEMS actuator? UniversityWafer provides research-grade wafers with custom doping, thickness, and orientation for electrostatic, thermal, and piezoelectric designs.
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Get MEMS Actuator Wafers Fast
UniversityWafer, Inc. supplies research and production wafers optimized for MEMS actuator fabrication — from early-stage prototyping to full wafer-level packaging.
- Silicon & SOI wafers (100–300 mm)
- Piezoelectric materials: LiNbO₃, LiTaO₃, PZT
- High-strength options: SiC, sapphire, and quartz
- Custom thicknesses, dopant types, and orientations
- Mirror-polished or etched surfaces for MEMS micromachining
Every wafer ships with traceable specs and quality documentation to meet your MEMS actuator design goals.
What We Offer
We provide small-lot and volume orders for MEMS fabrication labs worldwide. Engineers choose us for reliable wafer flatness, low defect density, and fast lead times. Our substrates support:
- Electrostatic & comb-drive actuator prototypes
- Piezoelectric micro-pumps and resonators
- Thermal and magnetic micro-motors
- Integrated MEMS-CMOS designs
Looking for bonded stacks or metallized wafers? Explore our bonding services or contact us for a custom quote.
Typical Specs Available
| Wafer Type | Diameter | Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Si (100) | 100–300 mm | 200–675 µm |
| SOI | 100–200 mm | Handle 500 µm / Device 10–50 µm |
| LiNbO₃ / LiTaO₃ | 2–4 in | 0.5–1 mm |
| SiC | 50–150 mm | Up to 1 mm |
Need non-standard parameters? Our engineering team can source wafers built to your exact actuator design.
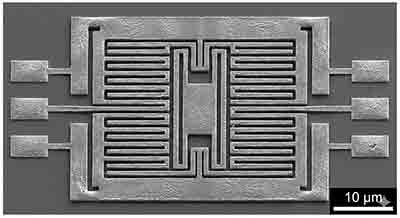
How Do MEMS Actuators Work?
MEMS actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion at the microscale. Built on the same wafer as sensors and control circuits, these devices form the active, moving components in micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) used across optics, RF, biomedical, and automotive industries.
The Core Principle
In a MEMS actuator, tiny mechanical structures—such as beams, diaphragms, or comb drives—respond to electrical input by moving, bending, or vibrating. Because these components are fabricated using semiconductor microfabrication techniques, actuators can achieve nanometer-level precision in both force and displacement.
Main Actuation Mechanisms
MEMS actuators operate through several physical effects, each with unique benefits and material needs:
- Electrostatic Actuators – Use the attraction between charged electrodes. Common in silicon-based comb drives and micro-mirrors.
- Piezoelectric Actuators – Rely on materials like LiNbO3, LiTaO3, or PZT that deform when voltage is applied—ideal for precision optics and acoustics.
- Thermal Actuators – Use Joule heating and expansion to move micro-structures; excellent for larger displacements.
- Magnetic Actuators – Generate motion from magnetic forces; used in micro-motors and high-force applications.
Materials & Substrate Selection
The substrate wafer determines how the actuator performs under stress, temperature, and repeated motion. UniversityWafer provides wafers engineered for MEMS development, including:
- Silicon (Si) – The industry standard for bulk and surface micromachining.
- Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) – Enables precise definition of movable layers and mechanical isolation.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) – High-strength, high-temperature material for robust actuators.
- Quartz and Sapphire – Electrically insulating with excellent dimensional stability.
- Piezoelectric wafers – PZT, LiNbO₃, and LiTaO₃ enable voltage-driven deformation.
Fabrication Insights
MEMS actuators are produced by combining micromachining, thin-film deposition, etching, and wafer bonding steps. In thermal actuators, for example, polysilicon beams are doped and patterned to expand under current flow, while electrostatic comb drives are defined through deep reactive-ion etching (DRIE). Proper wafer flatness, thickness uniformity, and crystal orientation are essential to maintain performance across dies.
Performance Factors
- Displacement range – Set by geometry and actuation principle.
- Response time – Faster for electrostatic and piezoelectric designs.
- Force output – Higher for thermal and magnetic mechanisms.
- Power consumption – Optimized by substrate conductivity and heat dissipation.
Applications
MEMS actuators enable precision motion in multiple fields:
- Optical MEMS – Micro-mirrors, laser scanners, adaptive optics.
- RF MEMS – Tunable capacitors and high-frequency switches.
- Biomedical Systems – Micro-valves, tactile sensors, cell manipulators.
- Automotive – Inertial sensors, micro-pumps, and control actuators.
Why Partner with UniversityWafer
UniversityWafer, Inc. supplies research-grade and production-scale wafers for MEMS actuator prototyping and manufacturing. Our offerings include custom wafer diameters (50 mm–300 mm), controlled resistivity, SOI thickness tuning, and specialized coatings for MEMS processes. By sourcing through us, engineers and researchers gain access to materials optimized for actuation precision, thermal stability, and long-term reliability.
Design Considerations for MEMS Actuators
Successful MEMS actuator design balances performance with manufacturability. Key parameters—such as electrode geometry, beam dimensions, and anchoring design—must be optimized for desired displacement, frequency response, and energy efficiency. Finite element simulations (FEM) are often used to evaluate stress and thermal gradients before fabrication.
- Geometry: Comb drives deliver linear motion, while folded beams provide large strokes in compact layouts.
- Doping & Resistivity: Controls conductivity and heat generation in electrothermal actuators.
- Anchor Design: Determines mechanical stiffness and heat dissipation into the substrate.
- Packaging: MEMS actuators often require hermetic or vacuum sealing for stable performance.
Reliability and Lifetime
Because MEMS actuators operate through repeated motion cycles, material fatigue and thermal drift become critical over time. Substrate choice directly affects reliability—SiC and quartz substrates offer superior thermal stability compared to traditional silicon. Surface treatments and anti-stiction coatings also extend actuator lifetime.
UniversityWafer can source wafers with low-defect surfaces and controlled oxide layers that help mitigate electrostatic charging and mechanical wear in moving structures.
Fabrication Examples
Depending on the actuator type, fabrication may combine bulk and surface micromachining. For instance, a thermal bent-beam actuator can be formed from doped polysilicon layers etched above a sacrificial oxide, while a piezoelectric micro-mirror might use bonded SOI wafers with patterned electrodes and PZT films. Controlling wafer planarity and layer thickness uniformity is vital for repeatable motion and yield.
We routinely supply handle and device wafers for bonding processes that define free-standing MEMS structures, supporting DRIE and LPCVD steps with high precision.
Emerging Trends in MEMS Actuation
Recent advances are pushing MEMS actuators toward new materials and hybrid functions:
- 2D materials like graphene and MoS₂ for ultra-thin, low-voltage actuation.
- MEMS-integrated optics (MOEMS) for adaptive photonics and LiDAR systems.
- Soft MEMS that combine elastomers with silicon for bio-compatible devices.
- Energy harvesting actuators converting vibration into electrical energy for autonomous sensors.
As applications evolve, substrate innovation remains key. UniversityWafer continues to expand its offerings of piezoelectric, SOI, and compound wafers to meet the precision and integration demands of next-generation MEMS actuators.
Summary
MEMS actuators are the heart of microsystems — transforming electrical control into mechanical precision. Their performance depends not only on smart design but on the substrate foundation that supports every movement. With UniversityWafer’s extensive catalog of silicon, SOI, and specialty materials, engineers can confidently develop actuators that move faster, last longer, and perform reliably in demanding environments.
Contact us today to request a quote or discuss substrate selection for your MEMS actuator project. Get Your Quote Fast!
