PZT Wafers Used to Fabricate Actuators
A PhD student requested a quote for the following.
Would it be possible to provide an price estimate for:
- A single pzt deposited wafer between top and bottom electrode to be used for transducers (sensors and actuators).
- The top one but already transferred and packaged for ready-to-use applications.
- Also, does the buyer need to provide the transducer design for patterning it on the wafer? Or they could work with your engineering team to design it, and it is part of the cost estimate.
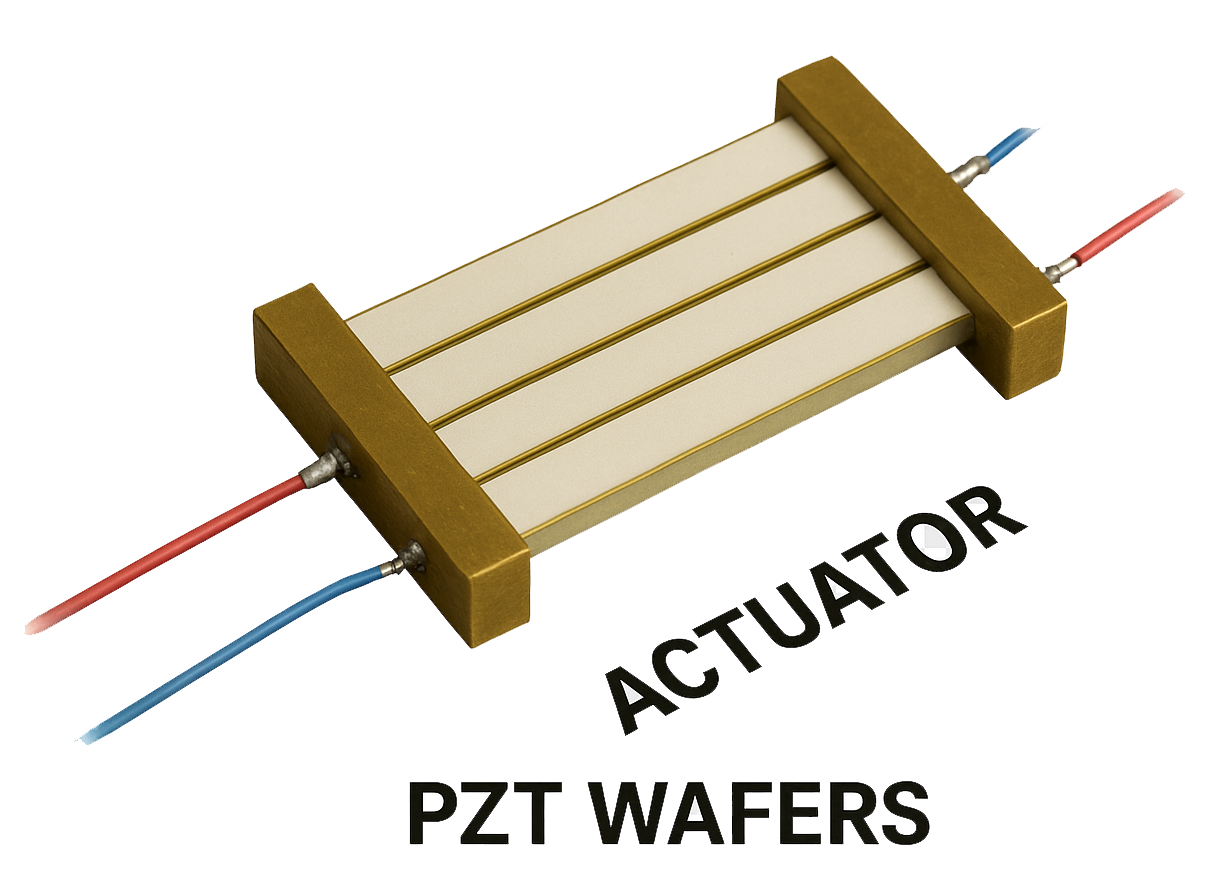
Reference #321507 for specs and pricing.
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Piezo Disc Actuator On Glass Wafer
A graduate student requested the following quote.
I am interested in using a low or room temperature bonding process to join a piezo disc actuator onto a ULE glass substrate. The disc actuator is of PZT-5H or PZT-5A (or LiNbO3) material, about 15 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick with a coaxial electrode Au coating. I'd like to prove the concept of using such a process, so would like to bond a single actuator onto a 100 mm diameter, 10 mm thick ULE substrate (with an Au pattern for the actuator).
Do you think this is possible with one of your processes?
Reference #322584 for specs and pricing.
Lithium Niobate Substrates Used To Fabricate Actuators
A hardware engineer requested a quote for the following.
Do you sell Lithium Niobate piezo actuators or just the raw material? We are trying to find a source for Lithium Niobate to be used in the 150 MHz + frequency range.
Reference #292605 for specs and pricing.
What Substrates Are Used To Fabricate Actuators?
An assitant professor at a large university requested a quote for the following.
Our lab is focused on MEMS devices. We usually use silicon and glass wafers for fabricating sensors and actuators.
We are currently looking for low resistivity (0.001-0.005 Ohm.cm) 4" silicon prime wafers, with 1µm of wet thermal oxide on both sides, similar to item 1583 in your catalog. But in our case, we would rather to have a DSP silicon wafers (instead of the SSP silicon wafers of the item 1583). Is it possible to customize this item to our needs? Our idea is to buy up to 50 wafers, depending on the price.
Reference #255029 for specs and pricing.
Substrates Most Commonly Used to Fabricate Actuators?
Actuators are devices that convert electrical, thermal, or other forms of energy into mechanical motion. The choice of substrate in actuator fabrication depends on the type of actuator (electrostatic, piezoelectric, thermal, etc.), performance requirements, and integration with other systems (e.g., MEMS, CMOS). Here are the most commonly used substrates for fabricating actuators:
🧱 1. Silicon (Si)
-
Most common substrate for MEMS actuators.
-
Compatible with standard semiconductor processing.
-
Suitable for electrostatic, thermal, and piezoresistive actuators.
-
Can be processed to make flexures, cantilevers, and membranes.
Example: Microgrippers, microvalves, micromirrors (e.g., DMDs).
🔬 2. Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI)
-
Ideal for high-precision MEMS actuators where electrical isolation or defined layer thickness is important.
-
Reduces parasitic capacitance, improves thermal isolation.
-
Useful in electrostatic comb-drive or piezoelectric layer-on-SOI actuators.
🔋 3. Piezoelectric Substrates
Example: Micropumps, inkjet print heads, RF switches.
-
Often used when optical transparency or electrical insulation is needed.
-
Quartz is also piezoelectric, so it can serve dual functions.
🧊 5. Polymers (e.g., PDMS, SU-8)
-
Used for flexible or soft actuators.
-
Beneficial for biomedical applications (e.g., artificial muscles, microfluidics).
-
Can be combined with embedded electrodes or thermal expansion mechanisms.
🔥 6. Metals and Metal Foils (e.g., Nickel, Titanium)
Summary Table:
| Actuator Type |
Common Substrates |
Notes |
| Electrostatic |
Silicon, SOI |
MEMS-compatible |
| Piezoelectric |
PZT, AlN, ZnO, SOI |
Thin films often deposited on Si |
| Thermal |
Silicon, Polyimide |
Thermal expansion or bimorphs |
| Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) |
NiTi, Si with SMA layer |
Deforms under heat |
| Soft/Bio Actuators |
PDMS, SU-8, Hydrogels |
Soft robotics, microfluidics |
If you’re targeting a specific application (e.g., biomedical, aerospace, RF MEMS), I can recommend the best substrate options based on constraints like temperature, flexibility, cost, and integration.

