Ultra-Pure Float Zone Silicon Wafers
NEWS! Soon we will be offering Float Zone Silicon that are only 5 micron thin! Contact us if you want to be notified when we receive the new inventory.Float zone Silicon or FZ is the purest form of silicon available. Thus it's much more expensive than silicon grown using the Czochralski method. However, even though FZ Si is more expensive, it's still the least expensive Infrared material available. FZ Silicon provides better than 50% transmission in the 1.5 to 6 micron wavelength.
Float-zone silicon is typically used for high-efficiency solar panels, power devices and detector applications. It is highly transparent to terahertz radiation, and is usually used to fabricate optical components, such as lenses and windows, for terahertz applications.
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
Unlock High Purity & Performance: Exclusive Float Zone (FZ) Inventory
At UniversityWafer.com, we understand that standard Czochralski (CZ) silicon simply doesn't cut it for high-efficiency, high-voltage, or high-frequency applications. That is why we have curated one of the most extensive inventories of Float Zone (FZ) silicon wafers available on the market today.
From 1 inch to 8 inch (and select 12 inch options), we stock the hard-to-find purities and resistivities your projects demand—available for immediate delivery.
Why Float Zone?
Float Zone silicon offers superior purity (extremely low Oxygen and Carbon content) and precise dopant uniformity. This makes it the material of choice for power devices, detectors, and high-frequency RF applications where signal loss and carrier lifetime are critical.
5 Key Applications by Resistivity Range
1. Low Resistivity FZ (< 100 Ω-cm)
Ideal for high-efficiency energy conversion and standard power switching.
- High-Efficiency Solar Cells: Used in Interdigitated Back Contact (IBC) and HIT cells where minority carrier lifetime is crucial.
- Power Diodes & Rectifiers: Provides the uniform resistivity needed for consistent breakdown voltages.
- Discrete Power Transistors: Essential for low-noise audio transistors and switching components.
- Hall Effect Sensors: Offers crystal perfection for sensitive magnetic field detection.
- MEMS Actuators: Provides a mechanically superior substrate for precise micro-movements.

2. Mid-Range High Resistivity (> 1,000 Ω-cm)
The standard for power handling and improved RF performance.
- IGBTs: The backbone of electric vehicles, requiring FZ purity to handle high voltages without latch-up.
- RF MEMS Switches: Reduces insertion loss and improves isolation compared to CZ silicon.
- Optical Position Sensors: High purity allows for faster response times and lower leakage currents.
- Thyristors: Critical for high-power switching applications in power grids.
- High-Voltage MOSFETs: Enables devices that can switch hundreds of volts with minimal on-resistance.
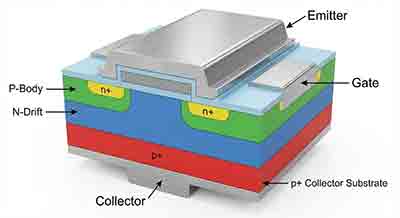
3. High Resistivity (> 5,000 Ω-cm)
Entering the realm of particle physics and low-loss RF.
- Silicon Drift Detectors (SDDs): Used in X-ray spectroscopy for low capacitance and high energy resolution.
- Particle Strip Detectors: Essential for high-energy physics experiments to track charged particles.
- RFIC Substrates: Significantly reduces substrate coupling and parasitic capacitance.
- Deep Depletion Photodiodes: Allows for a wider depletion region, increasing sensitivity to Near-Infrared.
- Coplanar Waveguides (CPW): Minimizes dielectric loss for microwave signal transmission.

4. Very High Resistivity (> 10,000 Ω-cm)
Critical for microwave and faint-signal detection.
- Microwave Monolithic Integrated Circuits (MMICs): A cost-effective, high-performance solution for GHz frequency bands.
- High-Speed Photodetectors: Low capacitance allows for ultra-fast response times.
- Avalanche Photodiodes (APDs): Low defect density reduces dark count rates, essential for low-light detection.
- Passive RF Components: High-Q inductors and capacitors integrated directly onto the silicon.
- Nuclear Radiation Detectors: Used for detecting alpha and beta particles with high background rejection.
5. Ultra-High Resistivity (> 20,000 Ω-cm)
The "Holy Grail" of silicon substrates for scientific and quantum applications.
- Terahertz (THz) Optics & Imaging: Highly transparent to Terahertz radiation; ideal for windows or lenses.
- Cryogenic Physics Experiments: Used for devices operating at mK temperatures to avoid carrier freeze-out.
- Quantum Computing Substrates: Provides a quiet electrical environment for superconducting qubits.
- Far-Infrared (FIR) Components: Used in astronomy for lenses requiring minimal FIR absorption.
- Single-Photon Detectors: Extreme purity minimizes trap states for quantum cryptography.

Featured Inventory Ready to Ship
Below is a selection of our in-stock Float Zone silicon. Request a Quote.
Low Resistivity (< 100 Ω-cm)
| Item # | Diameter | Type | Resistivity (Ω-cm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12852 | 8" | p-type Si:B | 1-50 | Prime, TTV<5μm |
| 11507 | 6" | n-type Si:P | 3-4 | PV FZ, High Lifetime |
| B0206 | 6" | p-type Si:B | 1-30 | Prime, Back-Side LaserMark |
| 12535 | 4" | n-type Si:P | 1-5 | PV Prime, MCC >2,000μs |
Mid-Range High Resistivity (> 1,000 Ω-cm)
| Item # | Diameter | Type | Resistivity (Ω-cm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8297 | 8" | p-type Si:B | 2,000-6,000 | Prime, MCC Lifetime >1,000μs |
| 4982 | 6" | n-type Si:P | >1,000 | Prime, Front-side LaserMark |
| 5729 | 5" | p-type Si:B | >1,000 | Prime, Front LM |
| 5744 | 5" | p-type Si:B | >1,000 | SEMI Standard |
| G158 | 4" | n-type Si:P | >1,000 | Prime, TTV <2μm |
High Resistivity (> 5,000 Ω-cm)
| Item # | Diameter | Type | Resistivity (Ω-cm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10507 | 6" | p-type Si:B | >8,000 | Prime, 400μm thick |
| B208 | 6" | n-type Si:P | >9,500 | Prime, MCC >6,000μs |
| E239 | 6" | n-type Si:P | 7,000-8,000 | MCC Lifetime = 7,562μs |
| 12648 | 4" | n-type Si:P | >5,000 | Prime, 200μm thick |
| 12489 | 4" | n-type Si:P | 5,000-20,000 | Prime, MCC >1,000μs |
Very High Resistivity (> 10,000 Ω-cm)
| Item # | Diameter | Type | Resistivity (Ω-cm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1417 | 8" | Intrinsic | >10,000 | Prime, MCC >1,000μs |
| 12111 | 6" | Intrinsic | >10,000 | Prime, TTV <5μm |
| A1557 | 4" | Intrinsic | >10,000 | Prime, TTV <5μm |
| 11073 | 4" | p-type Si:B | >10,000 | Prime, Particle Count <20 |
Ultra-High Resistivity (> 20,000 Ω-cm)
| Item # | Diameter | Type | Resistivity (Ω-cm) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10938 | 8" | Intrinsic | >20,000 | Prime, MCC >1,000μs |
| D817 | 6" | Intrinsic | >65,000 | Prime, Notch |
| 12070 | 4" | Intrinsic | >20,000 | Range up to 189,900 Ω-cm |
| 12030 | 3" | Intrinsic | >20,000 | Prime, TTV <5μm |
Float Zone Silicon Wafers for Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
Researcher asked for the following:
"I am trying to find Silicon wafers for a professor who wants to use them with Infrared Spectroscopy measurements. His requirements are: For IR I am having more trouble finding a suitable option. I have previously used lightly doped (Boron) double-side polished p-type Si substrates with resistivity >3000 Ω cm. I think I can get away with resistivity >1000 Ω cm."
UniversityWafer Quoted and Client Purchased:
Thickness around 500 micron, Diameter 100 mm, double-side polished, resistivity >1000 Ω cm.
Please contact us for pricing.
Float Zone (FZ) Silicon Wafer Facts
If you are looking for the best type of wafer you need for your next project, then you need to look at FZ wafers. The superior properties they bring are highlighted in many applications and are therefore described as a good alternative to CZ wafers. According to a recent study by the Institute of Electrical and Computer Engineers (IEC) at the University of California, San Diego, it is recommended to use an FZ wafer.
FZ wafers are said to have a vertical melting process through which pure silicon flows. Pfann has developed a method to avoid contamination of silicon. The presence of light and impurities such as nitrogen improves the mechanical performance of the wafer and also helps to control micro-defects.
FZ wafers are extremely transparent to radiation such as terahertz, making them a compact wafer specifically designed for use in high-power, low-energy applications.
Full General Inventory List
| FZ Si Dia | Type/Dopant | Ori | Resistivity Ohm-cm | Polish | Thickness (Microns) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25.4mm | Undoped | (100) | >2,000 | SSP | 280 | Intrinsic Float Zone |
| 50.8mm | N/Ph | (111) | >200 | SSP | 200 | 2 FLats back-side Alkaline etched |
| 76.2mm | Undoped | (100) | >5,000 | SSP | 500 | Undoped Float Zone |
| 100mm | P/B | (111) | 40-60 | SSP | 255 | Buy as few as one |
| 150mm | Undoped | (100) | >10,000 | DSP | 650um | Hard to Find |
| 200mm | Undoped | (100) | >1,000 | SSP | 725um | FZ SI TTV <6um |
