Do you sell wafers that have Through Silicon Vias in them? We are looking for up to 5 wafers with TSV’s in them. Wafer must be doped 1 – 500 Ohms in that range somewhere.
What Is Through-Silicon Vias?
Wafers With Through Silicon Vias
A PhD candidate requested a quote for the following. Find out how we helped them!
Reference #162771 for specs and pricing.
Get Your FAST! Or, Buy Online and Start Researching Today!
What is the purpose of Through Silicon Via (TSV)?
The purpose of Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) is to create vertical electrical connections that enable efficient and compact integration of multiple chips or components within a single package, thereby enhancing device performance, reducing power consumption, and enabling new functionalities in electronics. Below are the specific purposes:
1. High-Density Interconnects
TSVs provide a way to connect multiple layers of chips directly through the silicon substrate, eliminating the need for long horizontal wiring. This leads to:
- Reduced interconnect length
- Increased interconnect density
- Faster communication between layers
2. Enabling 3D Integration
TSVs are fundamental to 3D ICs, where multiple chips or wafers (e.g., logic, memory, sensors) are stacked vertically. This allows:
- Compact packaging: Reduces overall size and weight of devices.
- Heterogeneous integration: Combines different technologies (e.g., CMOS logic with memory or MEMS) in a single package.
- Enhanced functionality: Improves performance by integrating more capabilities in a smaller form factor.
3. Improved Performance
By providing direct and shorter paths for signals, TSVs help:
- Reduce signal delay
- Lower power consumption
- Increase bandwidth This is especially important in high-performance computing, graphics processors, and AI accelerators.
4. Advanced Packaging
TSVs play a key role in System-in-Package (SiP) and 2.5D interposer technology:
- SiP: Integrates multiple functions (e.g., logic and memory) in a single package.
- Interposers: TSVs in silicon interposers connect chips side-by-side in high-performance 2.5D configurations.
5. Enhanced Thermal Management
In some applications, TSVs can be used to facilitate heat dissipation, improving thermal performance in densely packed systems.
6. MEMS and Sensors
TSVs are essential in MEMS devices and sensor systems, where they enable compact designs and efficient signal routing for applications like accelerometers, gyroscopes, and imaging sensors.
Use Cases
- Smartphones: For memory stacking (e.g., DRAM on top of a processor).
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): Enables 3D integration of CPUs, GPUs, and memory.
- Image Sensors: Stacking image sensor arrays with logic circuits.
- IoT Devices: Reduces form factors while enhancing functionality.
In summary, TSVs enable advanced electronics packaging technologies, driving improvements in miniaturization, performance, and power efficiency across various industries.
What Is Through-Silicon Vias?
Through-Silicon Vias (TSVs) are vertical electrical connections that pass through a silicon wafer or die, enabling high-density interconnections between stacked dies in a 3D integrated circuit (3D IC). TSVs are a key technology in advanced semiconductor manufacturing, enabling efficient communication and power distribution in compact, multi-layered device architectures.
Key Features of TSVs:
- Structure: TSVs are typically cylindrical holes etched through the silicon substrate, filled with a
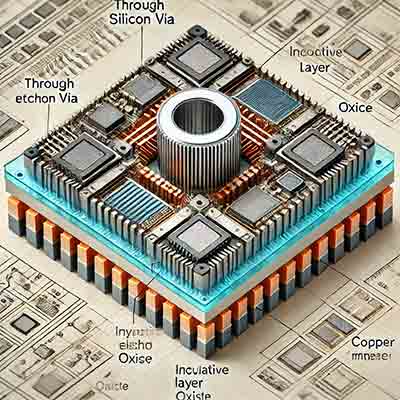 conductive material (e.g., copper or tungsten) to form an electrical path.
conductive material (e.g., copper or tungsten) to form an electrical path. - Diameter: They range in size from a few micrometers (for advanced designs) to tens of micrometers (for simpler designs).
- Depth: The depth depends on the wafer thickness and the specific application, often in the range of tens to hundreds of micrometers.
Applications:
- 3D Stacked ICs: TSVs enable vertical stacking of chips such as processors, memory, and sensors, improving performance and reducing power consumption.
- MEMS Devices: Used in Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) for compact, high-performance packaging.
- Interposers: Found in 2.5D packaging, where a silicon interposer with TSVs connects multiple chips on a substrate.
Benefits:
- Compact Designs: Reduces the overall size of electronic devices by eliminating the need for long interconnects.
- High Bandwidth: Enables faster communication between layers due to shorter signal paths.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower power consumption because of reduced signal delay and lower resistance.
- Improved Performance: Facilitates integration of different technologies (e.g., CMOS, memory) into a single package.
Challenges:
- Manufacturing Complexity: Fabrication of TSVs involves precise etching, insulating, and filling processes, increasing production costs.
- Thermal Management: 3D stacking can lead to heat dissipation challenges.
- Reliability: Mechanical stress and potential for voids in the conductive fill material can impact device reliability.
TSVs are a cornerstone technology for modern electronics, enabling innovations in compact, high-performance devices such as smartphones, high-performance computing systems, and advanced sensor applications.
What is Power Through Silicon Via?
A Power Through-Silicon Via (Power TSV) is a specialized type of through-silicon via designed to deliver power or ground connections vertically through a silicon substrate in 3D integrated circuits (3D ICs). These vias are critical for distributing power efficiently to various layers of a stacked chip, complementing signal TSVs that are primarily used for data communication.
Purpose of Power TSVs
- Efficient Power Delivery: Provide a direct, low-resistance path for power and ground, reducing voltage drops and power losses.
- Compact Integration: Enable efficient vertical power delivery in 3D-stacked chips, saving space compared to traditional wire bonding or flip-chip connections.
- Thermal Management: Help in distributing heat by acting as thermal conduits in addition to their electrical function.
- Improved Signal Integrity: By separating power and ground paths from signal TSVs, Power TSVs reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve the performance of high-speed circuits.
Structure of Power TSVs
- Larger Diameter: Typically larger than signal TSVs to handle higher current densities and reduce electrical resistance.
- Materials: Conductive materials like copper are commonly used for their low resistance and high current-carrying capacity.
- Isolation: Surrounded by an insulating layer (e.g., silicon dioxide) to prevent electrical leakage into the silicon substrate.
Applications
- 3D IC Power Distribution: Used in stacked processor-memory systems to supply power efficiently to all layers.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): Deliver stable power in dense, high-current environments such as CPUs and GPUs.
- Mobile Devices: Support compact designs with efficient power delivery for processors and memory in smartphones and tablets.
- System-on-Chip (SoC): Power TSVs are integral in multi-functional SoCs that require robust power delivery to different functional blocks.
Advantages of Power TSVs
- Reduced Power Loss: Direct paths through silicon minimize resistance and power dissipation.
- Improved Power Density: Enable high-current delivery in compact 3D structures.
- Enhanced Device Performance: Maintain stable voltage levels, reducing noise and improving overall performance.
- Smaller Form Factor: Allow for more compact device packaging compared to traditional power distribution methods.
Challenges
- Thermal Stress: High current flow can lead to joule heating, requiring effective thermal management.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Fabrication of larger, low-resistance vias with precise alignment adds complexity and cost.
- Reliability: Handling high current densities requires robust materials and designs to avoid electromigration and mechanical failures.
In summary, Power TSVs are essential for delivering power and ground connections efficiently in advanced 3D integrated circuits, enabling compact, high-performance electronic systems.
