50.8mm P/B <100> 1-10 280um SSP Prime w/ 5000nm (5um) silicon
dioxide thin film used for research and development of optical
waveguides.
What Substrates are Used for Optical Waveguide Research?
2 Inch Silicon Wafers Used to Fabricate Optical Waveguides
a microfabrication cleanlab facility manager requested a quote for the following.
Reference #91787 for specs and pricing.
SOI Wafers to Fabricate Optical Waveguides
A PhD student requested the following:
I have received my SOI wafer. It has 250nm silicon layer with 2um oxide layer beneath. We will use it to fabricate silicon optical waveguide.
BTW, do you have any information of cutting/cleaving SOI wafer? We are not sure if it is just the same as cleaving the common silicon wafer in lab? by the diamond pen is ok?
Reference #47079
Get Your Quote FAST! Or, Buy Online and start researching today!
SOI Platform to Fabricate Optical Waveguides
A graduate student requested a quote for the following:
I am working in integrated photonics and I am trying to make optical waveguides using an SOI platform. I need to purchase an SOI wafer but I was wondering if you know what doping level/resistivity would be appropriate for optical waveguide fabrication? My understanding is that a highly doped wafer would create losses due to the free carriers, so I am wondering if I need to use a wafer which has no doping? I thought to ask you because maybe you have dealt with this before for other customers. I am looking for a device layer thickness of 220-250nm, Ori <100>, bottom oxide layer 2-3um, diameter 150mm. I'm just not sure what doping works best for photonic applications.
I am really just wondering if you know if the doping of the device layer will negatively affect the propagation loss in SOI waveguides. For example, you currently have a wafer in stock with ID 3381 which is 150mm diameter, P type doping, <100> Ori, 220nm device layer thickness and 2um BOX layer thickness. The resistivity is listed as 10-20 ohm-cm, which I believe corresponds to about 10^15 doping concentration (correct me if I'm wrong). This is the wafer I have been using in my experiments so far, but I am wondering if that doping is causing any propagation loss. I am trying to minimize propagation loss by adjusting my fabrication steps, but maybe I also need to use an undoped wafer to further reduce my propagation loss? Do you know if your other customers are using this doping concentration in SOI waveguides?
Reference #259923 for specs and pricing.
Low Dopant Concentrations for Optical Waveguides
A PhD Candidate requested the following pricing.
These are for optical waveguides in Si. Lower dopant concentrations are best (~10^15, B). I'd like a quote for a range of device layer thicknesses (1um - 4um).
4" P/B (10^15/cm3) (100)
We quoted:
p-type Nc 10E15/cc corresponds to 12 Ohmcm.
We can offer such wafers. We offer:
Item Qty. Description
T19. 10/25 Silicon wafers, per SEMI, P/P 4"Ø×525±25µm,
p-type Si:B[100], Ro=(30-80)Ohmcm,
Both-sides-polished, SEMI Flats.
Reference #100388 for specs and pricing.
SOI Wafers for Optical Communications Research
An optical researcher requited a quote for the following:
I need a quotation for a SOI wafer with the dimensional characteristics showed in the attached file. The Ori must be 100, and the diameter, if possible, 2" or 3". This wafer will be used to construct a silicon waveguide to work in the optical communications C or L band (from 1530 to 1610 nm).
Reference #111529 for specs and pricing.
Oxide and Nitride Coated Silicon for Structuring Optical Waveguides
I am interested in ordering Wafers with the following specification.
Substrate:
Material: Silicon
Diamter: 4''
Crystal Ori: 100
Thickness: 525 ľm
Doping: P
Dopant: Bor
Conductivity: 0-30 Ohmcm
First Layer:
Material: Silicon oxide (SiO2)
Thickness: 4000 nm
Second Layer:
Material: Silicon nitride (Si3N4)
Thickness: 750 nm
Prefered Method: LPCVD
The wafers are meant for structuring optical waveguides in the
siliconnitride so actually the substrate material does not really
matter and I would prefer to order the cheapest silicon substrate
available.
Reference #121685 for specs and pricing.
What is an Optical Waveguide?
An optical waveguide is a physical structure designed to guide electromagnetic waves, particularly optical frequencies (such as visible, infrared, or ultraviolet light), along a defined path. Waveguides achieve this by confining and directing light through total internal reflection, ensuring minimal loss of optical energy as it propagates.
Structure and Composition:
- Core: Central region with a higher refractive index.
- Cladding: Outer layers surrounding the core, possessing a lower refractive index.
- Substrate: Often provides mechanical support and may be part of the structure.
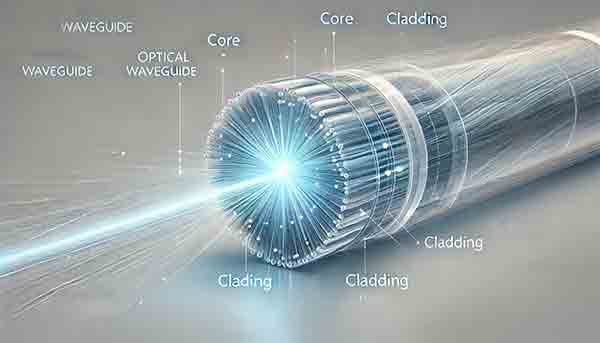
Principle of Operation:
Optical waveguides guide light by exploiting the principle of total internal reflection (TIR):
- Light injected into the core remains trapped, reflecting repeatedly at the core-cladding boundary due to the difference in refractive indices.
Types of Optical Waveguides:
-
Planar waveguides:
- Flat, rectangular structures often used in integrated optical circuits.
- Examples: Silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguides.
-
Channel waveguides:
- Confine light in two dimensions, creating a defined channel.
- Examples: Ridge, rib, and buried channel waveguides.
-
Optical fibers:
- Cylindrical waveguides with circular cross-section.
- Widely used for telecommunications, data transmission, and sensing.
Applications:
- Telecommunications and data transfer (fiber-optic cables).
- Integrated photonic circuits (optical computing, modulators, switches).
- Sensors and biosensors (chemical, biological, mechanical sensing).
- Lasers and optical amplification.
- Medical devices (endoscopes, minimally invasive diagnostics).
Advantages:
- Low signal loss and minimal interference.
- High bandwidth and data-carrying capacity.
- Small size and lightweight structure.
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
In summary, optical waveguides are crucial building blocks for modern optical communication systems, photonic integrated circuits, and sensing devices due to their ability to efficiently control and transmit optical signals over distances ranging from micrometers to thousands of kilometers.
What Substrates are used to Fabricate Optical Waveguides?
Optical waveguides are structures that guide light from one point to another, typically using the principle of total internal reflection. They are used in various devices like fiber optic cables and integrated optical circuits.
The choice of substrate used for fabrication of optical waveguides largely depends on the required properties such as optical transparency, refractive index, and mechanical and thermal stability. Various materials have been used to fabricate optical waveguides, including:
-
Silica (SiO2): This is one of the most common materials used for making fiber optic cables, which are a form of optical waveguide. Silica is preferred for its low loss at telecom wavelengths, high thermal stability, and robust mechanical properties.
-
Silicon (Si): Silicon is often used as the substrate in silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguides. The high refractive index contrast allows for tight bending radii, which is important for miniaturization in photonic integrated circuits.
-
Silicon Nitride (Si3N4): Silicon nitride is another commonly used material for fabricating waveguides, particularly for applications that require lower optical losses and broader wavelength operation than is typically achievable with silicon.
-
Polymers: Polymers such as PMMA (poly(methyl methacrylate)) or Ormocers can be used for the fabrication of optical waveguides, particularly for short distance communications, due to their ease of processing and ability to be directly written on.
-
Glasses: Certain types of glass, such as phosphate and chalcogenide glasses, can be used to fabricate waveguides. They are often chosen for their unique optical properties such as high nonlinearity or broad transmission windows.
-
Lithium Niobate (LiNbO3): Lithium niobate is a popular substrate for waveguides, particularly in applications that require high electro-optic coefficients, such as in modulators.
-
III-V Semiconductors: Semiconductors such as Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) and Indium Phosphide (InP) are used when active devices, such as lasers or amplifiers, need to be integrated into the waveguide.
In addition to these, other materials such as diamond, aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and various types of crystal materials (e.g., potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP), potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP), etc.) are used in specific applications.
Fused Silica Glass to Fabricate Optical Waveguides
A researcher from a large university engineering department requested the following:
My research group is looking to purchase fused silica wafer for optical waveguide fabrication. I was wondering what is the highest grade fused silica wafer available and what is its surface roughness. On the University Wafer website, it was mentioned that fused silica wafer (ID: 1943) can be used for optical grade experiments. I was wondering if you could let me know what is the surface roughness for this wafer as well.
Reference #276059 for specs and pricing.
Thermal Oxide Coated Silicon Wafers to Fabricate Optical Waveguides
A optical researcher requested the following quote:
Our main purposes is for educational and optics postgraduate program at our university. In particular, we have some Thesis projects related with basic synthesis
of submicron optical waveguides i.e. Al2O3, TiO2, etc. ) see atached
ref. And we are considering use Si wafer with SiO2 layer as sustrates.
Please send me the formal quotation for
Silicon 100mm P/B (100) 1-10 ohm-cm 500um SSP PRIME with 4um WET Thermal
Oxide
Reference #261959 for specs and quantity.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Substrates for Optical Waveguides
A postdoc requted the following information:
I just need a quotation of the various diameters of SiC wafers you have as we need for Project purpose
I would like to enquire more about SiC wafers. Do you have intrinsic SiC. I just want something that is smooth (optical quality on the polishing). Is their "mechanical quality" good enough? What is the roughness? We plan to make optical waveguides so I hope you understand the necessity of such details.
Reference # 100562 for specs and pricing.
Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) for Optical Waveguides
An optical device manufacturing requested a quote for the following:
We are looking for SOI wafer to build optical devices with 500~700nm top silicon layer and 1~3um buried oxide layer. The silicon layer is for building optical waveguides so we prefer non-doping is top silicon layer. Standard <1-0-0> is good for us. Please let us know the availability of this wafer and the quotation for 100mm and 150mm wafer if possible.
Reference #102779 for specs and pricing.
Thin Thermal Oxide Coated Silicon Wafers for Optical Waveguides
A optical phsysist requested a quote for the following:
This is an optical waveguide project that really needs 10 um oxide.
100mm Any Spec 500um SSP with 10 micron of thermal oxide
Reference #109609 for specs and pricing.
Fabrication of Optical Silica Waveguides
We are looking for silicon wafers that would be suitable for fabrication of optical silica waveguides. I think SSP prime wafers 4" with very low surface roughness would be best <1nm or better as a starting bare wafer. I don't know what coin roll grade is but I suspect it is a lower grade. Could you quote having 10um and 15um of thermal oxide?
Reference #111453 for specs and pricing.
